Most positive influence on orchard productivity
- Trying to stick to best practice pruning, etc. Punctual with interventions e.g. get spray on quickly after pest monitoring. Doing basics, not even well but just doing basics.
Most negative influence on orchard productivity
- Soil types could be better and wind can also be problematic.
General management
- Pollination, fertiliser planning and pest monitoring is contracted out. Remainder of work is completed by owners.
- A weather station in on-orchard with rainfall, temperature and wind used to inform orchard practices.
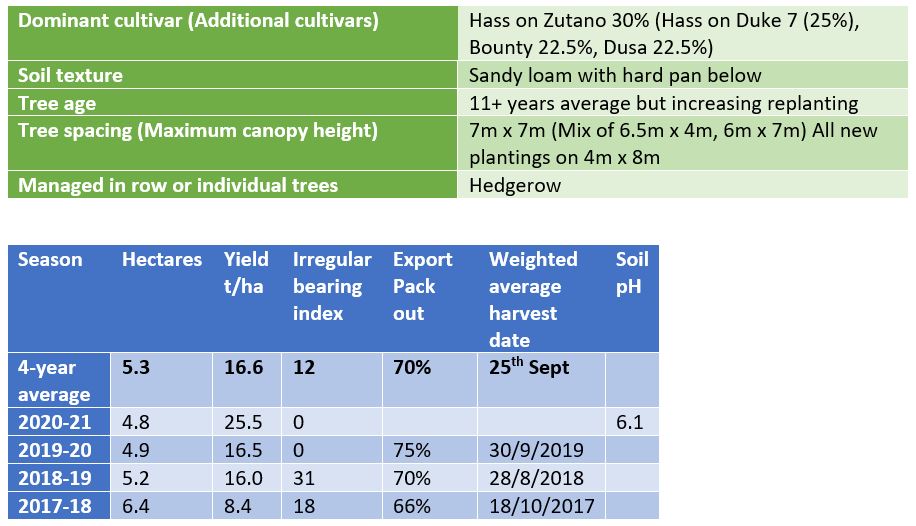
Canopy management
- Tree spaced 7m X 7m
- Managed in rows
- Max height of trees is 5-6m
- Priority when pruning is light interception followed by structural tree balance, increased access for picking and spraying, management of crop load and removal of dead or diseased material.
- Trees are structurally pruned once a year with pruning beginning in spring and whole orchard is generally finished by autumn.
- About 25% of the canopy is removed each year.
- Flower pruning and fruit thinning is used on excessively flowering trees and those that continue to carry excessive crops.
Soil and soil moisture management
- Orchard is predominately sandy loam with hard pan underneath that is broken on tree rows.
- Avocado pruning and leaf litter are used to mulch trees.
- Soil moisture is monitored at two sites with TDT sensors at 10cm, 30cm and 50cm as well as tensiometers. TDT readings of about 15% correlate with tensiometer reading of -20 to -30kPa for 10cm probe which is used as trigger for irrigation.
- The orchard is 100% irrigated with ground based microsprinklers.
- At peak summer it is common to irrigate for 2 hours per irrigation event once every 5 days using sprinklers with a 7.5m diameter that deliver 90l/hr (4.1mm per irrigation event)
- Sprinkler heads are chosen based on soil type, tree size and age and health. Irrigation is seasonally adjusted as well.
- Pump pressure and flow characteristics are checked at least annually with control valves, all pipework and sprinkler heads checked every irrigation.
Pollination
- Pollinizer species include Bacon, Ettinger, and Zutano at a percentage of 7-10%
- Hives are brought onto the orchard at about 30% flowering at a rate of 5-7 hives per hectare. Orchard often benefits from neighbours who have hives present earlier in flowering.
- Hives are located on the western side of most blocks where they get early morning sun.
Soil and fertiliser application
- Soil and leaf tests are carried out once a year in April.
- A consultant provides a fertiliser plan based on test results and crop loading.
- The majority of fertiliser is applied by ground application but foliar application is also used.
- Boron fertilisers are applied as ground application and foliar every year to maintain levels on sandy soil.
- Calcium fertiliser is applied when deficient.
- Fertiliser in some form is applied 12 times a year.
Tree health management
- Generally, 3 foliar phosphonate applications are made 2-6 weeks apart in late-summer to autumn. Root testing is carried out to verify application has been successful.
Frost protection
- No frost protection is in place in the orchard.