Most positive influence on orchard performance
- Good pollination with warm humid weather has helped. Pruning last year is helping a lot as well. Spending more time on orchard which believe is also helping productivity.
Most negative influence on orchard performance
- Not really any can think of.
General management
- Pollination, pruning and fertiliser planning pest monitoring and spraying is contracted out. Remainder of work is completed by owners. Using chicken manure more recently and have backed off nitrogen and other fertilisers to account for this.
Canopy management
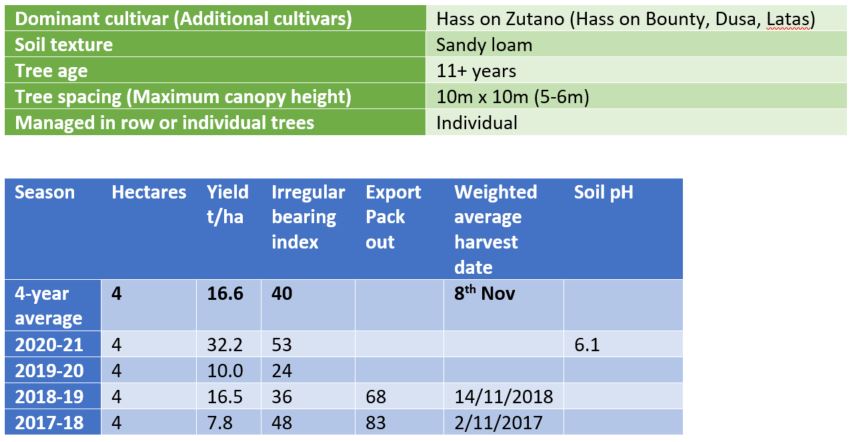
- Tree spaced 10m X 10m
- Managed as individual
- Max height of trees is 5-6m
- Structural tree balance is the main priority when pruning followed by increasing access for picking and spraying, management of crop load, light interception and removal of dead or diseased material.
- Trees are structurally pruned twice a year with larger cuts made in spring or autumn depending on crop remaining on trees. About 25% of the canopy is removed each year.
- Flower pruning is used on excessively flowering trees. Very rare to prune fruit off trees as regularly flower prune and generally get this right but will revisit if trees looking too stressed or carrying a heavy crop post flower pruning. Regular structural pruning helps regulate crop loading as well by maintain different aged wood and encouraging replacement wood.
- Crop load is assessed in stages with intervention made if not enough leaf is coming through. Possible that two rounds of flower pruning and 2 rounds of fruit pruning carried out on a tree if it continues to look stressed. Important to balance new fruit with flush, etc.
Soil and soil moisture management
- Orchard is predominately sandy loam.
- Grass cover is the dominant ground cover under trees, avocado pruning are used to mulch trees.
- Soil moisture is monitored using tensiometers and a Sentek probe. Tensiometer readings of -40kPa for 15-30cm probe which is used as trigger for irrigation in summer and autumn.
- The orchard is 100% irrigated with ground based sprinkler and over-canopy micro sprinklers used for frost protection.
- At peak summer it is common to irrigate for 8 hours per irrigation event less than once a fortnight using sprinklers with a 6m diameter that deliver 90l/hr (6.4mm per irrigation event). Bore available with consented water.
- Sprinkler heads that distribute different volumes over different area are chosen based on tree size and age.
- Pump pressure and flow characteristics are checked annually with ongoing inspection of pipework on orchard. Sprinklers heads are monitored regularly and serviced if required to maintain proper function.
Pollination
- Pollinizer species include Bacon, Ettinger, Zutano, Fuerte and Edranol at a percentage of 10-12%
- Hives are brought onto the orchard at about 5 – 10% flowering at a rate of 5-7 hives per hectare. Hives are located where they are accessible.
Soil and fertiliser application
- Soil and leaf tests are carried out once a year in April.
- A consultant provides a fertiliser plan based on test results and crop loading.
- The majority of fertiliser is applied by ground application but foliar application is also used.
- Boron fertilisers are applied as ground application and foliar every year.
- Lime and Gypsum (Calcium) fertiliser is applied every year.
- Fertiliser in some form is applied 20 times a year.
Tree health management
Trees are injected twice a year. Root testing of phosphonate levels are not carried out. All trees are injected in autumn and sick or stressed trees are reinjected in early spring.
Frost protection
Over canopy sprinklers are used for frost protection.